Equipment manufacturers, engineering, procurement and construction (EPC) companies, and power and process plant owners and operators commonly face the challenge of keeping their fleet, machinery, and other assets working efficiently while reducing the cost of maintenance and time-sensitive repairs. Considering the aggressive time-to-market required for industrial products and services, it is crucial to identify the cause of potential faults or failures before they have an opportunity to occur.
Emerging technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT), Big Data analytics, and cloud data storage are enabling more vehicles, industrial equipment, and assembly robots to send condition-based data to a centralized server. This makes fault detection easier, more practical, and more direct.
By proactively identifying potential issues, companies can deploy their maintenance services more effectively and improve equipment up-time. The critical features that help to predict faults or failures are often buried in structured data such as year of production, make, model, warranty details, as well as other unstructured data. The latter comprises but—isn’t limited to—information from log entries, sensors, error notifications, pressure, currents, voltage, odometer readings, and engine power-torque specifications.
Predictive maintenance is the process of generating advanced data analytics, which is derived from such sources can be turned into meaningful and actionable insights for proactive maintenance of assets, thereby preventing incidents that result in asset downtime or accidents. This process enables organizations to forecast when or if functional equipment will fail so that its maintenance and repair can be scheduled before the failure occurs.
North America Tops Market Share
Due to higher IT spending by companies looking to optimize operating costs and increase profitability, North America will continue to be the biggest market for predictive maintenance solutions. With an estimated market share of 31.67%, North America is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 24.5%, (see chart 1) maintaining its lead from 2017 through 2022. Key players include Bosch, GE, Hitachi, Honeywell, and Rockwell Automation.
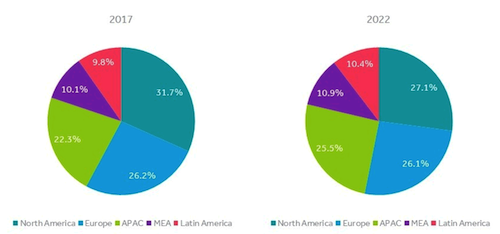
Predictive maintenance market share 2017-2022. Courtesy: Cyient
Increasing Product Availability
The underlying architecture of a preventive maintenance model is fairly uniform irrespective of its end applications. The analytics usually reside on a host of IT platforms, but these layers are systematically described as:
- Data acquisition
- Data transformation—conversion of raw data for machine learning models
- Condition monitoring—alerts based on asset operating limits
- Asset health evaluation—generating diagnostic records based on trend analysis if asset health has already started declining
- Prognostics—generating predictions of failure through machine learning models, and estimating remaining life
- Decision support system—recommendations of best actions
- Human interface layer—making all information accessible in an easy-to-understand format.
As industrial customers become increasingly aware of the growing maintenance costs and downtime caused by the unexpected machinery failures, predictive maintenance solutions are gaining even more traction. The manufacturing, energy, and utilities verticals are among the biggest demand drivers for predictive maintenance. This means it’s even more critical for equipment manufacturers, EPCs, and owners/operators to adopt a predictive maintenance solution to maintain a competitive advantage.
The bigger players have already been using this methodology for more than a decade. Small- and medium-sized companies in the manufacturing sector also can reap its advantages by keeping repair costs low and meeting initial operational costs for new operations.
While it offers more business benefits than corrective maintenance, predictive maintenance is also a step ahead of preventive maintenance because maintenance work is scheduled at preset intervals and intended to reduce the probability of failure or the degradation of an asset’s functions.
Gain the Benefits
In addition to the advantages of controlling repair costs, avoiding warranty costs for failure recovery, reducing unplanned downtime and eliminating the causes of failure, predictive maintenance employs non-intrusive testing techniques to evaluate and compute asset performance trends. Additional methods may include thermodynamics, acoustics, vibration analysis, and infrared analysis, among others.
The continuous developments in Big Data, machine-to-machine (M2M) communication, and cloud technology have created new possibilities for the investigation of information derived from industrial assets. Condition monitoring in real time is viable thanks to inputs from sensors, actuators, and other control parameters.
What stakeholders need is a bankable analytics and engineering service partner who can help them leverage data science to not only predict embryonic asset failures, but to eliminate them altogether by taking action in a timely manner.
Dr. Sean Otto currently leads business development for Cyient’s Advanced Analytics team, focused on designing AI and Machine Learning models to improve the functionality and reliability of equipment and systems in healthcare.
LEARN MORE
|
|
View the original article and related content on Plant Engineering
|






Comments